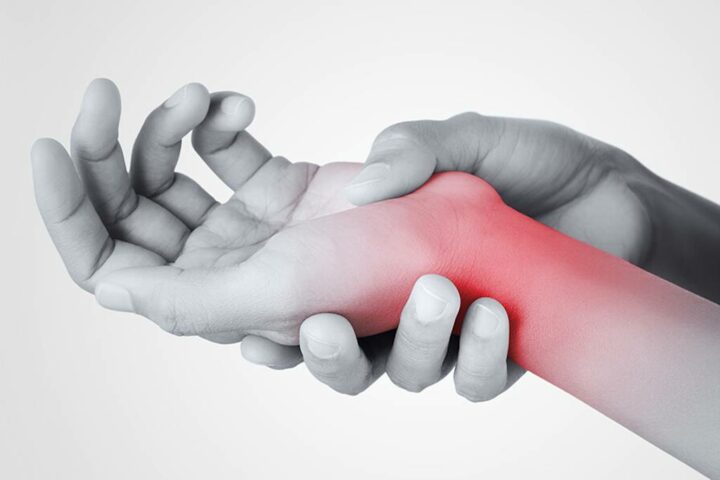
The carpal tunnel is a rather narrow channel located between the wrist and the hand. Inside it pass the tendons of as many as 9 muscles, as well as a nerve called the median nerve.
It is characterised by an empty space due to the anatomy of the carpal bones, which join the transverse ligament of the carpus.
Symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome (also known as ‘sdr carpal tunnel’) is caused by repeated compression of the carpal tunnel, resulting in inflammation.
The most common symptoms include:
– Pain in the wrist and fingers of the hand, most frequently in the right but sometimes also in the left (especially for left-handed people).
–Numbness and tingling, which may occur:
1.like a feeling of numb fingers;
2.with tingling in the first four fingers, from thumb to ring finger;
3.with numbness in the palm of the hand.
-In the most severe cases, severe pain in the hand that may develop into an intense burning sensation.
Carpal tunnel: causes
The causes of carpal tunnel syndrome can be various.
Increased pressure on the nerve, for example, can be caused by tenosynovitis, an inflammation of the sheath that surrounds the flexor tendons. This condition mainly affects women and can be promoted by factors such as joint dislocations or fractures.
During pregnancy (from the third month) and menopause, carpal tunnel occurs in many women due to hormonal changes, which cause water retention and swelling. This reduces the space inside the carpal tunnel, causing compression of the median nerve.
Certain diseases also favor the occurrence of inflammation:
● Diabetes: according to some clinical studies, diabetes predicts carpal tunnel syndrome, but the mechanism linking the two diseases is still unclear.
● Rheumatoid arthritis : sometimes it first manifests itself as carpal tunnel syndrome.
● Chronic water retention and renal insufficiency: both involve accumulation of fluid in certain areas of the body, including the hands and wrists.
● Hypothyroidism: complications of this condition include carpal tunnel and tarsal tunnel syndrome.
Finally, certain work activities such as daily computer and mouse use increase the risk of developing this disease.

Diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome
For the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome, it is necessary to consult medical specialists such as an orthopaedist or neurosurgeon.
Typically, the diagnosis involves an objective examination and an evaluation of the patient’s medical history and habits.
In some cases, however, electromyography is used, an examination which, in the case of carpal tunnel, involves inserting a small needle-electrode into the muscle.
The purpose of electromyography is to assess the speed at which the nerve transmits impulses and to check the health of the median nerve.
Other more specific carpal tunnel examinations are:
● The Tinel test, during which the doctor exerts light pressure on the patient’s wrist to check for tingling.
● The Phalen test, also known as the wrist flexion test, in which the patient must place their hands on top of each other on the side of the backs and with the fingers pointing downwards. Again, the purpose is to check for tingling sensations.
If from the objective examination it is feared that there is a wrist fracture or degenerative joint disease, then a radiological examination should be performed.
Similarly, if it is thought that the syndrome may have been caused by undiagnosed conditions such as diabetes, hypothyroidism or rheumatoid arthritis, blood tests are usually prescribed.
Now that we’ve talked about symptoms, causes, diagnosis and tests, you’re no doubt wondering what the ‘cure’ for carpal tunnel might be. Let’s get started!
Natural remedies for carpal tunnel
The most common natural remedies include:
● the simple application of ice, particularly when the wrist area is inflamed;
● performing carpal tunnel exercises, such as stretching or wrist strengthening exercises.
However, these exercises should always be performed under the supervision of a medical specialist, such as a physiotherapist or occupational physician.
When it is not possible to heal using simple natural remedies, one turns to more specific therapies.
Carpal tunnel therapies
Treatments for carpal tunnel syndrome depend on the duration and intensity of the symptoms.
In the following paragraphs, we will examine the different therapies, from the less invasive to the more invasive, in particular:
1. Conservative therapy for carpal tunnel
2. Instrumental physical therapy: magnetotherapy, electrostimulation, ultrasound therapy, laser therapy.
3. Carpal tunnel surgery
Conservative therapy for carpal tunnel
Conservative therapy involves the application of a brace to the wrist and the administration of anti-inflammatory drugs mainly based on corticosteroids. These drugs are taken orally or injected directly into the wrist.
In some cases, however, neurotrophic drugs are preferable to cortisone doses.
Treatment tends to be conservative, especially in pregnant women and particularly young patients.
Unfortunately, it is not always sufficient to cure the disease.
Magnetotherapy for carpal tunnel
Magnetotherapy (PEMF Therapy) is a non-invasive and effective technique for treating various conditions, including carpal tunnel syndrome. Through the use of low-frequency, high-intensity pulsed magnetic fields, this therapy stimulates cell recovery, reduces inflammation and improves local circulation, significantly alleviating pain. Clinical studies have shown that specific magnetotherapy programmes, based on targeted frequencies , can offer positive results in the treatment of carpal tunnel, promoting a rapid reduction of symptoms.
Among the most relevant research, the 2015 study ‘Pulsed magnetic fields vs. surgery‘ showed that pulsed magnetic fields improve electrophysiological function of the median nerve and increase functional abilities of the hand.
The study was conducted with one of our magnetotherapy devices.
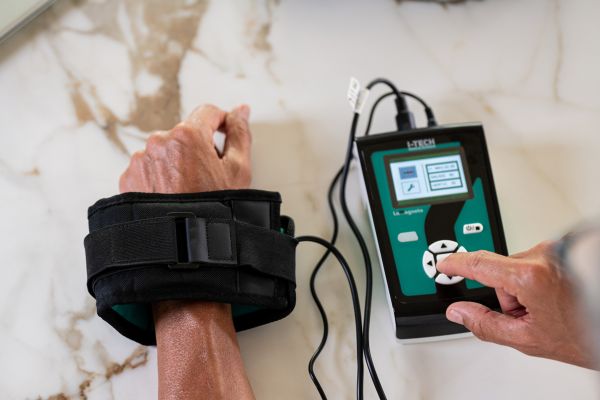

Electrostimulation for carpal tunnel
Electrostimulation is a technique that uses electrical impulses to simulate the action of the nervous system, activating muscles and stimulating nerve fibers. Thanks to the possibility of customizing intensity and frequency, this therapy can be used for anti-inflammatory, analgesic or rehabilitation purposes. In particular, TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation) programmes are effective in treating carpal tunnel, reducing pain, improving local circulation and relieving symptoms of inflammation. This technology represents a non-invasive option for improving hand function and patient well-being.
Click here to discover our entire range of certified medical devices for home use , for an electrotherapy session in the comfort of your own home.
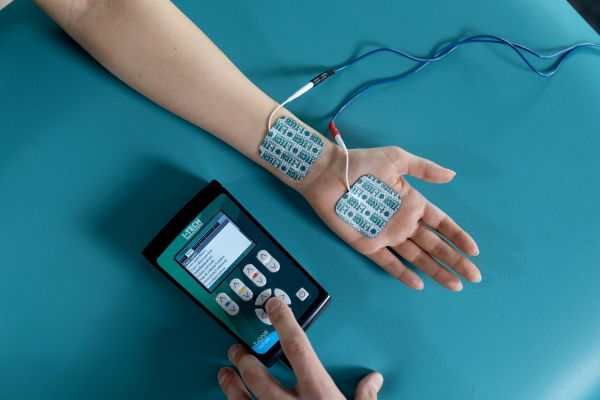

Ultrasound therapy for carpal tunnel
Ultrasound therapy is a widely used therapeutic technique for the treatment of musculoskeletal disorders, including carpal tunnel syndrome. By emitting high-frequency sound waves, ultrasound promotes a targeted action on deep tissue, providing analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects.
But what are ultrasound devices for carpal tunnel?
Among our range of devices, we cannot fail to mention Powersonic, the ultrasound therapy device certified for home use. Its ergonomics and the possibility of battery operation make it unique. With Powersonic you can have therapy wherever and whenever you want, reducing pain and inflammation in just a few sessions.
Our device can also be used in an outpatient setting, by a professional practitioner.
Whereas, our I-TECH UT2 and I-TECH UE ultrasound therapy devices are designed exclusively for the practice. Their versatility allows therapy to be adapted to patients’ needs, making them a viable solution for carpal tunnel treatment.
Laser therapy for carpal tunnel
Laser therapy is also one of the treatment options for carpal tunnel. Here too, the therapy must be carried out by a health professional.
Our I-TECH LA500 device, with an adjustable power of up to 500 mW and a wavelength of 810 nm, makes it possible to rapidly reduce pain and inflammation in patients suffering from this pathology, as well as in numerous arthro-rheumatic conditions, and, in general, in the fields of rehabilitation therapy, general medicine and dermatology.
Ultrasound and laser therapy were compared in a clinical study in which the effectiveness of the two therapeutic techniques in the treatment of idiopathic carpal tunnel was analyzed. After two weeks of therapy and analysis of 50 patients, the researchers stated that improvements were most noticeable in those who underwent ultrasound therapy, particularly in terms of: delay of movement, amplitude of motor action potential, grip strength and pain relief.
Carpal tunnel surgery
When the symptoms are too intense and have been present for at least six months, it is advisable to undergo carpal tunnel surgery.
The procedure involves cutting the band of tissue around the wrist. This reduces the compression on the median nerve.
Doctors may decide to perform two different types of surgery:
● a neurolysis operation, in which doctors make a single incision in the wrist of about 5 cm;
● an endoscopic operation, involving two incisions of just over 1 cm on the wrist and palm of the hand.
As a rule, both operations are performed under local anaesthesia, but endoscopic surgery allows faster rehabilitation.
Carpal tunnel convalescence
Immediately after surgery, the patient enters the convalescence phase. Initially, he or she must keep the wrist bandaged for a few days. Then it is recommended to start performing rehabilitation exercises using a carpal tunnel brace or cuff.
For optimal post-operative care, we share below what not to do after carpal tunnel surgery.
● Excessive exertion: do not lift weights or make repetitive movements with the operated hand.
● Skipping physiotherapy: essential for regaining strength and mobility.
● Prolonged immobility: avoid holding the hand too still to prevent joint stiffness.
● Ignore signs of infection: consult your doctor if you notice redness, swelling or intense pain.
How to prevent carpal tunnel syndrome?
As mentioned earlier, this syndrome can be linked to certain activities performed daily in the workplace.
This is why it is possible to take some steps to prevent it, such as stretching exercises and taking breaks during manual work.
In addition, you should always pay attention to both your body posture and wrist position.
Prevention is therefore very important because it can avoid having to undergo surgery in the future, also thanks to instrumental physical therapy.
Are you interested in learning more about our therapeutic techniques that can help you find relief from carpal tunnel pain?
Click the button below and get in touch with our customer care: a team of people always ready to listen to you and guide you in choosing the solution that best suits your needs. Don’t forget, however, to always consult your doctor.