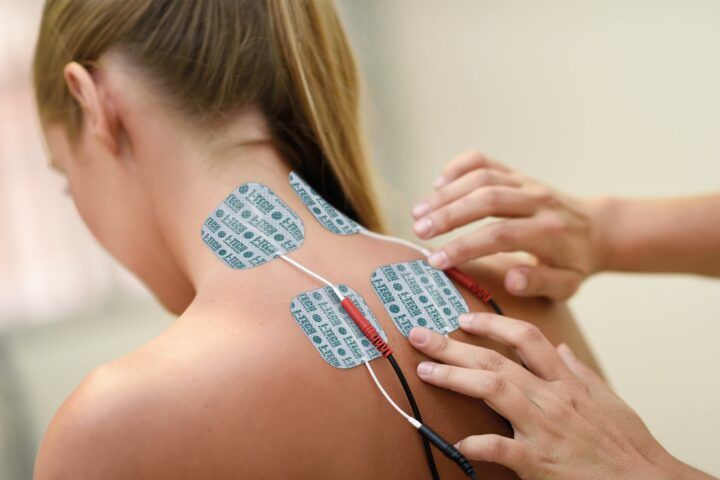
The acronym TENS stands for ‘Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation’. It is a technique of electrostimulation used for relieving pain by locally limiting the perception of pain caused by various pathologies.
This type of electric current has proven its effectiveness in the treatment of various pathologies, including:
· Neck pain
· Arthrosis
· Myalgia
· Neuritis
· Backache
· Periarthritis
· Headache
The main action of TENS stimulation is localised at the skin and subcutaneous level, exploiting the body’s ability to reduce the perception of pain as an effect of stimulation at the level of surface receptors, which are those on which TENS acts.
From a physiological point of view, the mechanism of this technique is quite complex. However, its application is simple and effective. The placement of the electrodes is very intuitive since, apart from occasional applications, it is done right on the pain area.
To learn more, we recommend you read this blog article that explains in a simple way the types of TENS and the benefits it can bring in the treatment of pain.
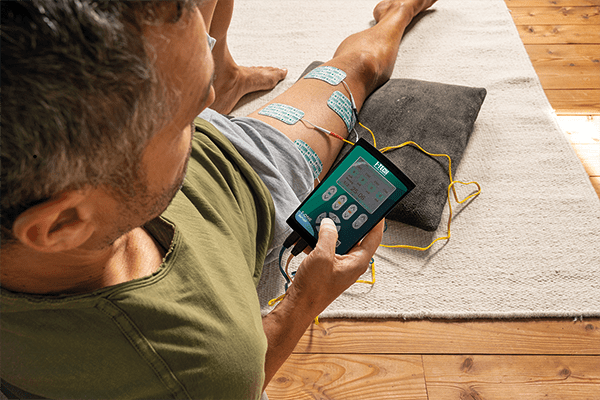

The main categories of TENS
On a general level, TENS therapy carried out at home for relieving pain can be classified into two different categories:
– Traditional TENS stimulation,
– Endorphine release stimulation.
The difference between these two categories lies in the timing of effectiveness. With the use of traditional TENS we can achieve results in the short term, with the use of endorphine stimulation, on the other hand, in the medium term.
The main applications of TENS therapy
As mentioned above, TENS therapy focuses its action on reducing pain through stimulation of skin receptors. Different programs can be used to achieve pain reduction, which differ in certain electrical parameters that optimise their effects.
– Conventional TENS
It is the classic method of applying TENS with standard parameters adapted to most pathologies. It aims at reducing the perception of pain, interrupting its circuit that would otherwise tend to cause antalgic contractures.
– Scanning TENS
It uses parameters similar to conventional TENS by inserting variations in certain electrical parameters of the stimulation, reducing the adaptation effect – this way the receptors do not get used to the stimulation.
It is particularly indicated for chronic problems or those that do not respond effectively to conventional TENS stimulation.
– TENS at maximum values
This programme uses similar parameters to those used in traditional TENS but at higher levels, with the advantage of being effective in a short time. This type of application can be useful for effectively reducing the perception of pain in a short time, although it is advisable to combine it with other methods in order to prolong its effects.
– Endorphins stimulation TENS
Endorphin stimulation aims to increase endogenous endorphin production. Compared to TENS stimulation, it has a longer-lasting effectiveness, although this is achieved over a longer period of time. For this reason, it may be useful to combine endorphin therapy with traditional TENS therapy, thereby optimising the timing of effectiveness of the two methods.
– TENS burst
TENS stimulation with burst pulses uses a particular modulation that alternates between emission and pause phases, with parameters that are similar to a combination of traditional TENS pulses and endorphin pulses.
TENS therapy: how to do the therapy
TENS stimulation is typically applied to painful areas. For it to be effective, it is useful that the sensation experienced during stimulation is pleasant.
To achieve this pleasant sensation, it is necessary that the intensity adjustment is not excessive; throughout the treatment period, the perception should be similar to that of a slight tingling sensation on the skin.
The intensity of stimulation, even if it remains constant, gradually tends to make the tissues get used to the current used on them, reducing the perception of tingling. Therefore, it is a good idea to gradually increase the intensity during the treatment, ensuring that the sensation is constant. Remember, however, that you should not see a contraction of the muscle.

TENS sessions: how long and how many to do
A single TENS session lasts on average about 20 minutes and can also be repeated several times a day. The treatment cycle lasts between 7 and 10 days. After this period, it is a good idea to interrupt for a few days to check the results obtained and, if necessary, repeat the cycle.
Precisely because of the possibility of repeating sessions daily and in several cycles, it is advantageous to have a TENS electrostimulator available for home use.
The advantages of TENS therapy
The different modalities of TENS in physiotherapy can be applied to various body districts regardless of the origin of the pain (traumatic, overload or stress). TENS current also does not require any specific adaptation depending on the body district.
In order to simplify the process of choosing which program to use, specific programs optimised for the main problems that can benefit from this type of therapy have been packaged:
– Neck pain
– Myointensive headache
– Low back pain
– Sciatica
– Sprains
– Bruises
– Vascularisation
– Muscle Relaxation
– Hematomas
– Hand and wrist pain
– Plantar stimulation
– Epicondylte
– Epitrocleitis
– Periarthritis
TENS anti-inflammatory
TENS stimulation does not have a direct anti-inflammatory effect, but by reducing the perception of pain, it helps reduce the processes that pain creates at the level of the muscles. Such as the onset of antalgic contractures, which in turn tend to reduce the inflow and reflux of blood, thus favouring the generation of inflammatory states. The anti-inflammatory effect of TENS, therefore, is indirect but effective.
TENS: placing the electrodes
The placement of electrodes is extremely simple since, in most cases, they are placed on the area of pain.
If you suffer from epicondylitis, the electrodes should be placed at the elbow, the same applies when treating a shoulder problem where the electrodes should be placed directly on the shoulder. What does this mean? The electrodes should be placed at the edge of the painful area so that the electric field develops its effects in the area between the electrodes.
Some problems, particularly at the cervical and lumbar levels, may require different positioning. For example, for cervical problems, especially if they cause headaches or pain at the base of the skull, the placement will be at the level of the neck, particularly at the back, at the sides of the spine, with two electrodes on each side.
Lumbar problems, especially of a sciatic nature, require the placement of electrodes at the lumbar level even if the pain occurs near the buttock or leg.

TENS: contraindications
TENS current therapy, even though it uses limited electrical parameters, is comparable to an electrotherapy; therefore, its use in total autonomy is not recommended to:
● Pacemaker wearers
● Patients with cardiopathy
● Epileptic patients
● People with neoplasms or tumours
● People suffering from active phlebitis or thrombophlebitis
● Pregnant women
● Muscle injuries
● Skin lesions in the treatment area
● Presence of inflammatory states
However, we always advise you to seek the advice of your doctor or the professional you are relying on before starting a TENS treatment, as, under their supervision, some of the conditions listed above may be revised.
TENS therapy at home
One of the undeniable advantages of TENS therapy is that it can be performed completely independently, in the comfort of home.
Thanks to certified medical devices, therapy at home is safe. There are simple and intuitive devices on the market: in just a few steps you can start your treatment. We always advise you to seek initial support from a professional in order to get the maximum effectiveness from your treatment. In this way you will also be more inclined to be more consistent with your sessions and achieve results in the short term.
We have been present in the electro-medical market for over 25 years, with a wide range of 2-channel and 4-channel electrotherapy devices including TENS electro-stimulators.