Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic and debilitating disease that primarily affects the joints, causing pain, swelling and stiffness. It is an autoimmune disease, in which the immune system affects joints and connective tissues [1] , leading to permanent damage if not treated promptly . But what are the symptoms to recognize? And what treatments can alleviate this condition? Let’s find out together in this comprehensive guide.
What is rheumatoid arthritis?
Rheumatoid arthritis is a systemic disease involving the immune system and manifested primarily by inflammation of the joints. The term “rheumatoid arthritis” denotes an autoimmune condition that can progressively worsen, leading to functional limitations and irreversible joint damage.
Rheumatoid arthritis: symptoms
Recognizing the early symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis is crucial for early diagnosis and effective treatment. Some of the main signs to watch for include:
- Joint stiffness: especially in the morning or after long periods of inactivity.
- Swelling and redness: joints appear swollen, warm, and sore.
- Persistent pain: worsens with movement and may limit daily activities.
- Chronic fatigue: feeling of exhaustion even after good rest.
- Mild fever and weight loss: systemic symptoms that may accompany inflammation.
Symptoms by body area
- Feet: heel pain, deformity and difficulty walking.
- Hands: swelling of finger joints, stiffness and difficulty in fine movements.
- Arms: pain and limitation in movement.
- Knee: swelling, stiffness, and difficulty bending the joint.
- Shoulder: radiating pain and reduced range of motion.
- Wrist: difficulty rotating or bending the wrist, often with obvious swelling.
- Ankle: instability and pain that worsens when walking.
- Eyes: dryness, redness and inflammation (possible keratoconjunctivitis).
Causes of rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is caused by a combination of genetic, environmental and immunological factors, but which are the most common ones to watch out for?
- Genetic predisposition: mutations in genes that regulate the immune system.
- Environmental factors: exposure to infection or toxins.
- Hormonal imbalances: more common in women, often during periods of hormonal changes.
- Smoking: increases risk and worsens symptoms.
- Viral or bacterial infections: possible triggers of the autoimmune response.
Rheumatoid arthritis and Raynaud's syndrome
Often associated with rheumatoid arthritis, Raynaud’s syndrome manifests as an abnormal vascular response to cold or stress, causing pallor and pain in the fingers and toes.
In people with rheumatoid arthritis, Raynaud’s syndrome can be aggravated by chronic inflammation and joint damage, making vascular crises more frequent and intense. In some cases, reduced circulation can lead to complications, more or less serious if not managed in time.
Seronegative rheumatoid arthritis, what is it?
When blood tests do not detect rheumatoid factor or CCP antibodies but typical symptoms are present, it is called seronegative rheumatoid arthritis.
This form of arthritis can be more difficult to detect than the seropositive variant, but still requires early treatment to slow the course of the disease and prevent permanent joint damage. Therapies used to manage seronegative rheumatoid arthritis are similar to those for seropositive and include anti-inflammatory drugs physiotherapy treatments, among others. In these cases, however, it is more than advisable to get advice from a specialist.
Rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis
Rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis are two autoimmune conditions that, although different, can sometimes coexist or have similar symptoms, creating confusion in diagnosis. Psoriasis manifests as skin lesions, while rheumatoid arthritis affects the joints. In some cases, patients with psoriasis may develop psoriatic arthritis, a distinct form of inflammatory arthritis. For proper diagnosis and targeted treatment, it is important to distinguish between rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and psoriatic arthritis through clinical and instrumental examinations.
Rheumatoid arthritis: how the diagnosis is made
The diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis, to be as accurate as possible, requires a combination of:
- Blood tests: to detect rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-CCP antibodies.
- Instrumental examinations: x-rays, ultrasounds, or MRIs to assess joint damage.
- Rheumatology examination: to analyze the medical history and symptoms.
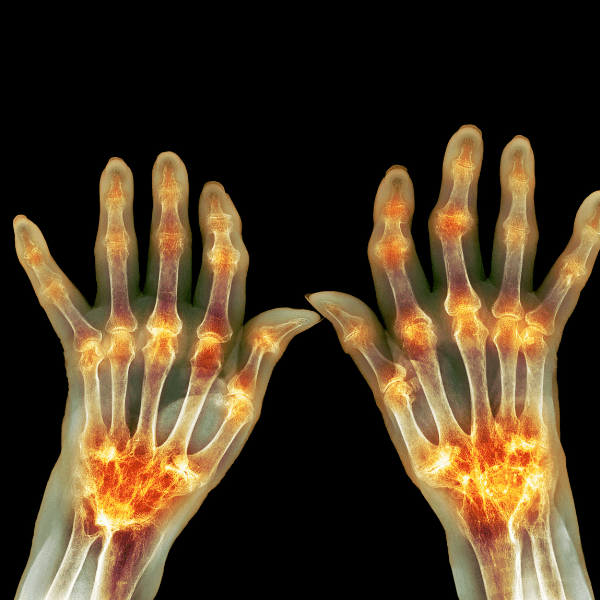
Rheumatoid arthritis: foods to avoid
In addition to the therapy/treatment indicated by the doctor, it is important to follow a diet consisting of foods that do not make one fat and that do not increase inflammation. Therefore, the following are not recommended:
- Red meat: can increase inflammation.
- Refined sugars: promote the accumulation of toxins.
- Alcohol and sodium-rich foods: worsen swelling.
- Gluten (if intolerant): can trigger an inflammatory response.
Magnetotherapy for Rheumatoid Arthritis: Benefits and Solutions
Magnetotherapy is a noninvasive therapy that is particularly effective in relieving the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis, a chronic condition that affects the joints. This technique uses low-frequency magnetic fields to stimulate microcirculation, reduce inflammation and relieve pain, offering concrete support to those seeking solutions to improve their quality of life.
With its ability to promote tissue recovery and improve joint mobility, magnetotherapy is a valuable ally in the daily management of rheumatoid arthritis. I-Tech Medical Division‘s devices are designed to meet these needs, with programs customized and easy to use even at home, making the therapy accessible to everyone.
Why choose magnetotherapy for rheumatoid arthritis?
- Reduction of pain and swelling: magnetic fields promote to decrease pain and slow down the degenerative process.
- Improved mobility: regular use helps reduce pain and improve mobility and quality of life.
- Safe and non-invasive therapy: ideal for prolonged treatment without significant side effects.
Before you begin, consult a specialist to choose the device and program best suited to your needs. Magnetotherapy is a natural and innovative option for dealing with rheumatoid arthritis and regaining daily well-being.
What products to choose to treat rheumatoid arthritis?
As we have seen, rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic condition that can significantly limit quality of life due to pain, inflammation, and motor difficulties. Fortunately, today there are several technological solutions that can support those suffering from this condition, improving symptom management and promoting joint wellness. Prominent among these are home and occupational therapy devices such as magnetotherapy, electrotherapy, and ultrasound therapy, which have proven effective in relieving pain and promoting recovery.
Magnetotherapy for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
PEMF (pulsed electromagnetic fields) magnetotherapy is a valuable aid in relieving pain and inflammation affecting bones, muscles, and joints. Pulsed electromagnetic fields promote rebalancing and proper cellular functioning, making it particularly suitable for treating traumatic and chronic conditions, including rheumatoid arthritis.
Our magnetotherapy devices feature preset, evidence-based programs designed to treat different conditions. The dedicated arthritis program helps reduce pain, slow the degenerative process and improve joint mobility. This solution is also ideal for the management of rheumatoid arthritis.
To find out more about magnetotherapy and its benefits, we refer you to the dedicated blog article.
Electrotherapy to combat rheumatoid arthritis
With our home devices , you can benefit from electrotherapy. from the comfort of your own home. This technology uses micro-pulses at different frequencies, intensities and amplitudes to speed recovery and relieve pain.
Electrostimulators with TENS programs, in particular, have an effective antalgic action, relieving pain and restoring physiological conditions. They are therefore suitable for the treatment of conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, which limit mobility. TENS not only reduces pain, but also promotes metabolism, blood circulation, oxygenation, and tissue nourishment. To maximize these effects, TENS can be combined with muscle stimulation.
Learn more about our electrostimulation devices! Read our in-depth review here.
Ultrasound therapy for rheumatoid arthritis
Ultrasound therapy is a technology that transfers energy to body tissues, having an analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect and stimulating tissue healing. This treatment can significantly improve the condition of rheumatoid arthritis sufferers, helping to reduce pain and inflammation
If your doctor has recommended that you undertake ultrasound therapy sessions, you will benefit from the therapeutic effects of ultrasound. Also, if you are considering purchasing a professional device for your practice that can also treat arthritis, visit our section I-TECH UT2 and I-TECH UE devices.
We hope you found this article helpful in understanding how to deal with rheumatoid arthritis and how I-Tech Medical Division products can help you do so!
Learn about our products by visiting our website on the Home Products page and find the right device for your needs!





