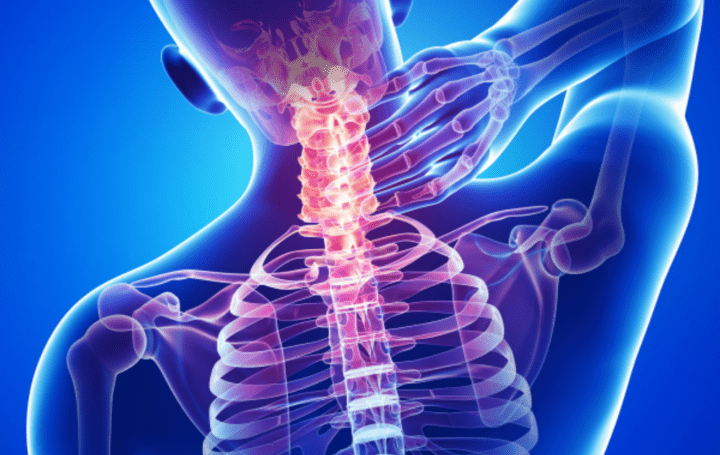
Cervical pain is pain that occurs in the neck and shoulder area, often caused by poor posture, muscle tension, or stress. This rather common disorder can restrict movement and impair quality of life.
However, there are several remedies and treatments to alleviate its symptoms and improve daily well-being. In this article we will look at what cervical pain is, what the most common causes are, and how it can be treated.
The symptoms of cervical pain
Cervical pain can manifest with a variety of symptoms that vary in intensity and duration, significantly affecting quality of life. Recognizing its signs is essential to intervene early and choose the most appropriate treatment.
- Neck and shoulder pain: The main symptom of cervical pain is persistent pain in the neck and shoulder area, which can vary in intensity and impair daily movements.
- Headache: Muscle tension caused by cervical pain can radiate toward the head, causing a localized headache in the neck area, sometimes extending to the forehead and temples.
- Nausea and dizziness: In severe cases, cervical pain can cause nausea and feelings of dizziness, often related to muscle tension affecting balance.
- Fever: Although rare, a slight rise in body temperature may accompany cervical pain, especially in the presence of inflammation.
- Neurological symptoms: Tingling, loss of sensation, or weakness in the arms and hands may indicate neurological symptoms related to cervical pain, caused by compression of cervical nerve roots.
- Posture and mobility disorders: Neck pain can restrict neck movement, causing stiffness and difficulty maintaining proper posture.
Cervical pain and lower back pain together: the symptoms
When cervical pain and low back pain occur simultaneously, the symptom picture can be more complex and debilitating, as it involves both the cervical (neck and shoulders) and lumbar (lower back) regions. This combination is often the result of poor posture, accumulated muscle tension, or degenerative spinal disease affecting both districts.
The main symptoms include:
- Persistent pain: Pain may involve the neck, shoulders, and lower back, intensifying after long periods in a sitting position or repetitive physical activities.
- Stiffness and difficulty in movement: The cervical and lumbar muscles are stiff and restricted, with greater difficulty in movement in the morning or after physical exertion.
- Tingling and weakness: Nerve compression, especially with inflammation, can generate tingling in the upper and lower limbs, accompanied by a feeling of muscle weakness.
Treating cervical pain and low back pain simultaneously requires an integrated and individualized approach, which often includes physical therapies, targeted postural exercises, and osteopathic or physical therapy treatments to improve spinal function and relieve symptoms.
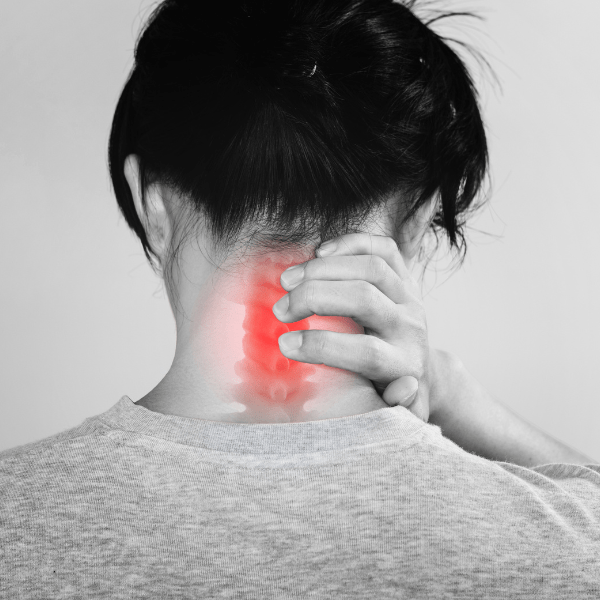
Cervical pain: the causes of pain
Neck pain, or cervical pain, can result from multiple factors that often act in combination, causing tension and inflammation in the neck and shoulder area. Knowing the main causes is essential to address and reduce the disorder. Some of the most common causes include:
- Poor posture: Maintaining non-ergonomic positions, especially for prolonged periods, can strain the neck muscles, causing tension and pain.
- Emotional stress and muscle tension: Psychological stress can contribute to constant contraction of neck and shoulder muscles, causing inflammation and stiffness.
- Physical trauma: Whiplash or direct injury to the neck, as in car accidents or falls, can damage tissues and cause cervical pain.
- Degenerative diseases: Conditions such as cervical osteoarthritis or degeneration of intervertebral discs increase the risk of chronic neck pain.
- Sedentary lifestyle: Lack of physical activity leads to weak postural muscles, exposing more to neck disorders.
Understanding the specific causes helps identify the best strategies to relieve pain and improve quality of life.
Stress neck, how long does it last?
Stress-induced cervical pain can vary in duration, depending on individual stress management and the adoption of relaxing measures. Often symptoms last from a few days to two weeks, but if the stress persists and is not treated, the pain can become chronic. Relaxation techniques, stretching and moderate physical activity can help reduce the duration of symptoms and prevent future relapse.
Cervical pain and dizziness, are they related?
Yes, cervical pain and dizziness are frequently linked. Neck pain can affect nerve and vascular structures located in the neck region, altering the sensation of balance and causing dizziness. Compression of cervical nerves can also irritate the balance centers, increasing the sensation of instability. If there is persistent dizziness, it is advisable to consult a physician to rule out other causes and plan appropriate treatment.
When does cervical pain become acute?
Cervical pain becomes acute when neck pain increases rapidly, causing stiffness and severely limiting daily movements.
This form often occurs as a result of sudden trauma, such as whiplash or a fall, but it can also arise due to poor postures maintained over time or from increased stress, leading to muscle tension and inflammation.
In the acute phase, pain may be accompanied by intense symptoms such as muscle spasms, headache, dizziness, and tingling in the upper limbs, a sign of possible cervical nerve compression.
It is recommended to rest and limit sudden movements, resort to targeted therapies such as physiotherapy, osteopathy or, if necessary, anti-inflammatory drugs under prescription to relieve pain and reduce inflammation, preventing cervical pain from becoming a chronic disorder.
Come curare la cervicalgia
Per trattare la cervicalgia è essenziale adottare un approccio combinato, che includa supporti ortopedici, terapie fisiche e, in alcuni casi, farmaci specifici.
- Cuscino per cervicalgia: Un cuscino ortopedico, progettato per sostenere la curva naturale del collo, aiuta a mantenere una postura corretta durante il sonno, riducendo il rischio di tensioni muscolari che contribuiscono al dolore cervicale.
- Fisioterapia cervicalgia: Gli interventi fisioterapici, come tecniche di massaggio e esercizi di mobilizzazione, sono efficaci nel ridurre la tensione e migliorare la flessibilità del collo. Affiancati da esercizi di stretching e rinforzo muscolare, i trattamenti aiutano ad alleviare il dolore e prevenire la ricomparsa dei sintomi.
- Antinfiammatori per cervicalgia: Nei casi acuti, possono essere indicati farmaci antinfiammatori non steroidei (FANS), come ibuprofene o naprossene, per alleviare l’infiammazione e il dolore. Tuttavia, è importante consultare un medico per valutarne l’idoneità.
Oltre ai rimedi qui elencati, anche terapie come magnetoterapia, elettroterapia e ultrasuonoterapia si sono dimostrate efficaci nel trattare questa problematica. Andiamo a scoprire di più nel prossimo paragrafo.
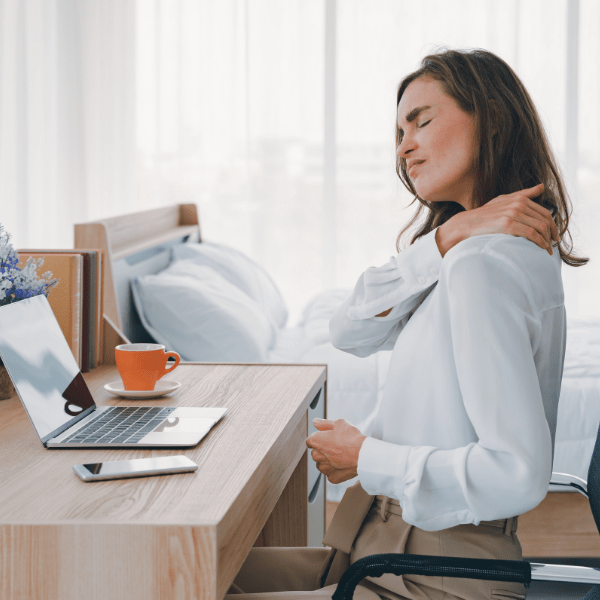

Therapy for cervical pain, is it a valid remedy?
Therapy for cervical pain is effective in reducing pain and improving neck function when tailored to the cause and severity of the disorder. Treatment may include physiotherapy, anti-inflammatory medications, and the use of ergonomic supports, such as an orthopedic pillow.
Physiotherapy is particularly helpful with muscle relaxation and joint mobilization techniques, often supplemented with stretching and strengthening exercises.
Among other types of therapy, magnetotherapy has been proven to be effective in the treatment of cervical pain . In a study evaluating its effectiveness on pain, joint range of motion, and functional status in patients with cervical osteoarthritis, significant improvements were found in pain, muscle spasm, and joint movements [1] [2].
Ultrasound therapy, for its part, is also an effective solution for reducing neck pain. Using high-frequency sound waves, this technique stimulates tissue regeneration, promotes microcirculation, and reduces inflammation[3] . Studies have been done for the treatment of muscle stiffness and chronic tension in the neck area where it is seen that ultrasound therapy in many cases helps to relax contracted muscles, speeding up recovery time and improving the quality of life of patients [4].
Electrotherapy is a noninvasive treatment for neck pain that uses electrical pulses to relieve pain and relax muscles. By stimulating nerve fibers, the therapy reduces pain perception, improves mobility and promotes the release of natural endorphins. This treatment can be great for those suffering from contractures and inflammation and is a viable option for those seeking relief from neck stiffness safely and effectively [5] [6].
Acting early on cervical pain with the right remedies can reduce pain and improve quality of life, limiting the impact of this problem on daily activities. For those who want practical and effective home support.
To discover all of our products, visit our I-Tech Medical Division home products page and find solutions designed to improve cervical wellness from the comfort of home!
Bibliography:
[1]“Efficiency of pulsed electromagnetic fields on pain, disability, anxiety, depression, and quality of life in patients with cervical disc herniation: a randomized controlled study” Hattapoglu Batmaz, Dilek Karacoc, Em, Cevik
[2]Karakaş M, Gök H. Effectiveness of pulsed electromagnetic field therapy on pain, functional status, and quality of life in patients with chronic non-specific neck pain: A prospective, randomized-controlled study. Turk J Phys Med Rehabil. 2020 May 18;66(2):140-146. doi: 10.5606/tftrd.2020.5169. PMID: 32760890; PMCID: PMC7401674.
[3] Qing W, Shi X, Zhang Q, Peng L, He C, Wei Q. Effect of Therapeutic Ultrasound for Neck Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2021 Nov;102(11):2219-2230. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2021.02.009. Epub 2021 Mar 17. PMID: 33722564.
[4] Therapeutic Ultrasound for Pain Management in Chronic Low Back Pain and Chronic Neck Pain: A Systematic Review; S.A. Noori, A. Rasheed, R. Aiyer, B. Jung, N. Bansal, K. Chang, E. Ottestad, A. Gulati
[5]González-Iglesias J, Fernández-de-las-Peñas C, Cleland JA, Alburquerque-Sendín F, Palomeque-del-Cerro L, Méndez-Sánchez R. Inclusion of thoracic spine thrust manipulation into an electro-therapy/thermal program for the management of patients with acute mechanical neck pain: a randomized clinical trial. Man Ther. 2009 Jun;14(3):306-13. doi: 10.1016/j.math.2008.04.006. Epub 2008 Aug 8. PMID: 18692428.
[6]Gemmell H, Hilland A. Immediate effect of electric point stimulation (TENS) in treating latent upper trapezius trigger points: a double blind randomised placebo-controlled trial. J Bodyw Mov Ther. 2011 Jul;15(3):348-54. doi: 10.1016/j.jbmt.2010.04.003. Epub 2010 May 13. PMID: 21665112.